This Information Security Awareness guide will reveal different types of computer security threats and recommended strategies for securing your personal and business data.
Table of Contents
Security Threats You Need To Know
Virus
A virus is a type of malicious software program that can replicate itself and infect a data on your computer.
Viruses tend to alter, damage or delete files and executable on your computer with the additional capability of erasing everything on your hard drive.
Your computer can become infected in a variety of ways, including via a downloaded email attachment, or on a USB drive so ensure proper security considerations when dealing with external files.
Spyware
A spyware is a type of malware that spies on your computer mostly as a background task and collects information without your knowledge.
A common example of a spyware is a keylogger software that records a your keystroke as you type your password and other personal/confidential information like your login details, and bank or credit account information.
Spywares are typically hidden from the user, and can be difficult to detect.
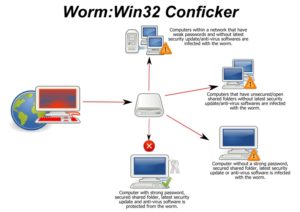
Worm
A computer worm is a form of malware that replicates itself and spreads to other computers within your network.
The Conficker worm is an example of an Internet worm that exploits your system’s vulnerability to infect other computers over the network.
Operating System vendors (e.g Microsoft: Windows 10, Apple: Mac OS X & RedHat: Linux) regularly issue security patches to fix vulnerabilities in their software which helps mitigate the spread of worms.
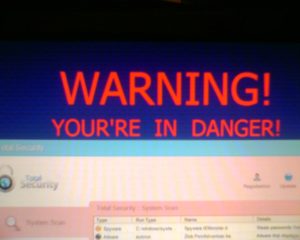
Ransomware
A Ransomware is a form of malicious software that encrypts the victim’s files, making them inaccessible, and demands a ransom payment to decrypt them.
A high-profile example of a Ransomware is “WannaCry” (also known as WCry, WanaCrypt) which infected over 230,000 Windows PCs in over 150 countries.
Ransomware commonly makes its way into a computer through the web or phishing emails when you click infected links or open an infected attachment.
Trojan
A Trojan is a malicious computer program that pretends to be a legitimate software, but actually executes hidden and harmful functions.
Trojans are generally spread by some form of social engineering, for example where a user is deceived into downloading and opening an infected e-mail attachment that appears to be unsuspicious.
Another example is a malicious link that says “Download to Win.” When you download and install the program, the Trojan infects your computer or deletes the data on your hard drive.
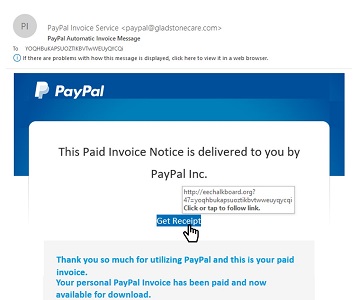
Phishing
A Phishing scam uses email, sms/text or social media to deceive a user into sharing personal and sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details with an unknown third party.
Phishing is typically carried out by sending an email that appears to come from a reputable organization, such as your bank to a user. It often directs you to enter your personal information on a fake website disguised as authentic.
To better protect against phishing attacks, it is a good practice not to click on links in email messages. Instead, you should type the website address in the address field of your browser and navigate to the intended page.
Rootkit
A rootkit is a malicious program designed to infect and gain “Administrator” or “root” access to a computer thereby granting full privilege to exploit the victim’s computer with the added ability to run as a background task and conceal it’s identity.
A rootkit can hide keystroke loggers or password sniffers programs in hidden locations on a system to capture confidential information and send it to hackers through the Internet.